Noise Induced Hearing Loss, Part 2
Last time I discussed the intensity of common sounds and some of the effects of noise exposure. Unlike many other types of hearing loss, noise induced hearing loss (NIHL) is preventable (National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders). This time I am going to explain steps you can take to protect your hearing from loud sounds.
When is noise dangerously loud?
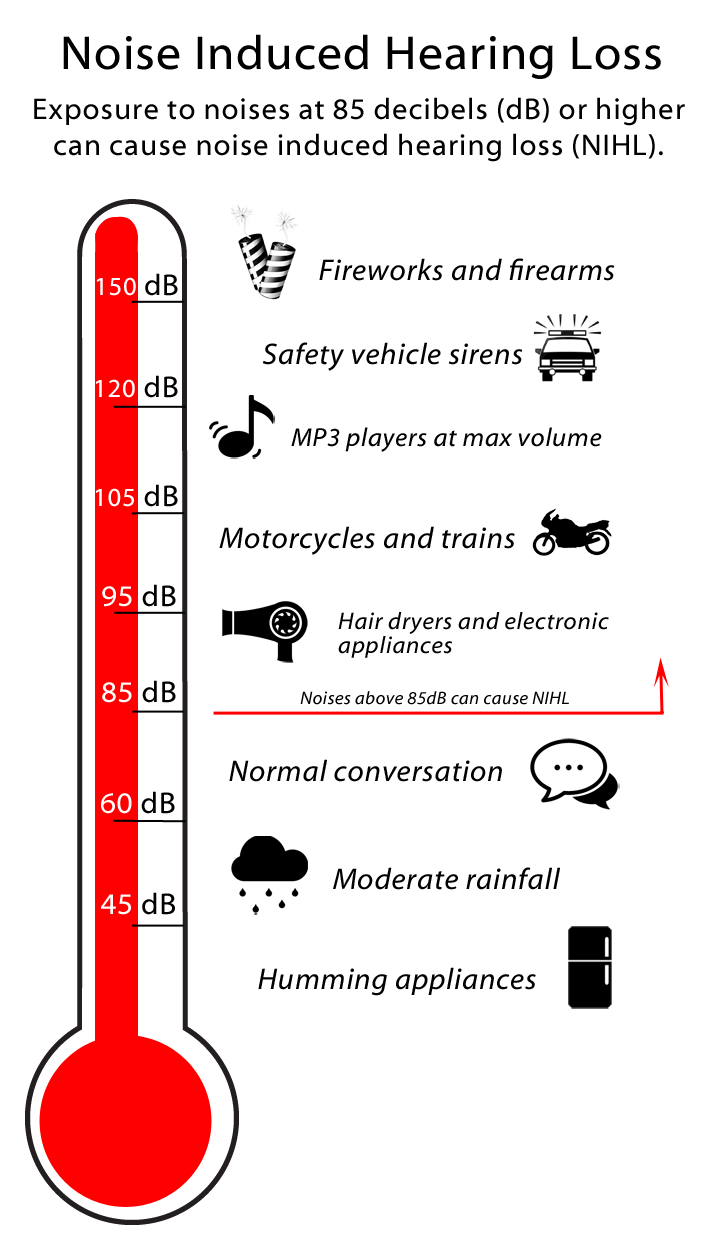
The first step in protecting your ears from noise is recognizing situations where noise is dangerously loud. Typically, the level at which sounds are damaging is 85 dB (NIDCD). A good rule of thumb to follow: if you must shout to be heard 3 feet away, the noise levels are probably ≥ 85 dB. Think of a noisy subway platform, shooting range, or arena packed with screaming fans.
How do I protect my ears from noise?
There are several strategies for protecting your ears from loud sounds:
- One strategy is to move away from the source of the noise (www.dangerousdecibels.org). As you move away from the noise’s source, the intensity decreases and therefore is less harmful to your hearing.
- A second strategy is to decrease the volume of the sound (www.dangerousdecibels.org). Many phones, MP3 players, and online music listening programs (e.g., Pandora and Spotify) allow you to set the maximum volume at a safe listening level, or alert you when the volume has been set to a dangerous level.
- Finally, use hearing protection if you often use noisy equipment, go to noisy places such as concerts, or are exposed to recreational noise from sources like engines or gunfire (www.dangerousdecibels.org).
What kinds of hearing protection are available?
Pre-molded rubber flange ear plugs (above) and foam ear plugs (below) are easy to find in most drugstores. Ear muffs can also be used as a form of hearing protection for those who find plugs uncomfortable or have other ear problems such as drainage or infection. When you use foam or rubber flange ear plugs, it is very important to insert them correctly to provide the most protection. Check out these resources for more information and instructional videos:
http://www.dangerousdecibels.org/about-us/the-solutions/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5nGO0qNTCd8
http://www.hearforever.org/faq
References




















Leave a Reply